Nutrition is important!
🍎 The Ultimate Guide to Nutrition Knowledge: Carbs, Protein, and Fat Explained! 💪
Understanding nutrition doesn’t have to be complicated! Let’s break down the three macronutrients and learn how to fuel your body like a pro. 🚀
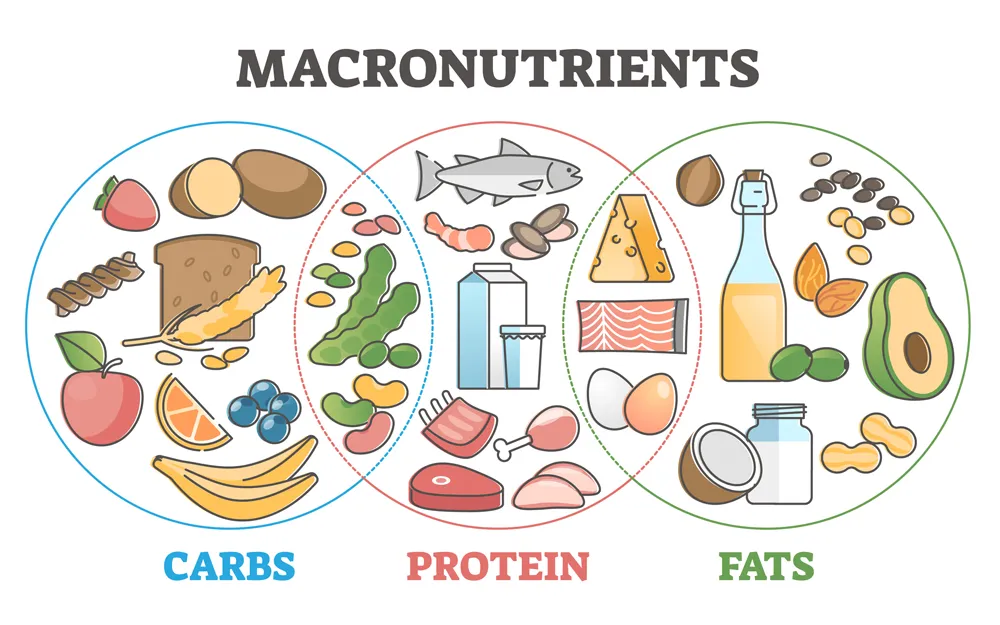
🍞 Carbohydrates: Your Body’s Primary Fuel Source
The Calorie Count 📊
1 gram of carbohydrates = 4 calories
Carbs often get a bad rap, but they’re actually essential for energy! The key is understanding which types to eat and when.
Types of Carbohydrates 🌾
1️⃣ Complex Carbohydrates (The Good Guys! ✅)
Complex carbs are long chains of sugar molecules that take time to break down, providing steady, sustained energy.
Found in:
- Whole grains (oats, quinoa, brown rice)
- Sweet potatoes 🍠
- Legumes (beans, lentils)
- Whole wheat bread and pasta
Why they’re better: Complex carbs digest slowly, keeping blood sugar stable and you feeling fuller longer! 😊
2️⃣ Simple Sugars (Use Wisely! ⚠️)
Let’s talk about the different types:
- Glucose 🍯 - The body’s preferred energy source; found in honey, fruits, and breaks down from other carbs
- Fructose 🍎 - Fruit sugar; found naturally in fruits and honey (good!) but also in high-fructose corn syrup (not so good!)
- Sucrose 🍬 - Table sugar; combination of glucose + fructose; found in processed foods and sweets
- Lactose 🥛 - Milk sugar; found in dairy products
Which ones are “bad”? It’s not that simple! Natural sugars in fruits and dairy come packaged with vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients. The problematic sugars are the added sugars in processed foods—sodas, candies, baked goods. These spike your blood sugar quickly without providing nutritional value. 📈
3️⃣ Fiber (The Unsung Hero! 🦸)
What is fiber? Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that your body can’t digest. It passes through your digestive system mostly intact.
Found in:
- Vegetables 🥦
- Fruits (especially with skin)
- Whole grains
- Nuts and seeds
- Legumes
Why don’t we count fiber calories? 🤔 Great question! While fiber technically has calories, your body doesn’t absorb them because it can’t break fiber down. That’s why many people subtract fiber from total carbs when counting “net carbs.” Fiber actually helps slow down sugar absorption and keeps you feeling full! 🎯
🍚 The Glycemic Index Issue: White Rice Example
White rice has a high glycemic index (GI) because:
- The outer bran and germ are removed (where fiber lives!)
- It’s mostly pure starch (simple carbohydrate)
- Digests rapidly → blood sugar spike → insulin surge → energy crash 😴
Brown rice is better because it retains the fiber-rich bran, slowing digestion and providing a more gradual energy release. 📉➡️📊
🥩 Protein: Your Body’s Building Blocks
The Calorie Count 📊
1 gram of protein = 4 calories
Amino Acids: The Protein Alphabet 🔤
Proteins are made of amino acids. Think of them as LEGO blocks that build everything in your body!
Essential Amino Acids (EAAs) ⭐
There are 9 essential amino acids your body cannot make on its own—you MUST get them from food:
- Histidine, Isoleucine, Leucine, Lysine, Methionine, Phenylalanine, Threonine, Tryptophan, Valine
Complete protein sources (contain all 9 EAAs):
- Meat, fish, poultry 🍗
- Eggs 🥚
- Dairy products 🧀
- Quinoa
- Soy products
Non-Essential Amino Acids 💚
Your body can synthesize these from other amino acids, so they’re “non-essential” in your diet (but still important!):
- Alanine, Asparagine, Aspartic acid, Glutamic acid, and others
Why Protein is AMAZING 💪
- Builds and repairs muscle tissue
- Creates enzymes and hormones
- Supports immune function
- Keeps you feeling full and satisfied
- Helps maintain lean body mass during weight loss
- Highest thermic effect (burns calories during digestion!)
🥑 Fat: Don’t Fear It, Embrace It!
The Calorie Count 📊
1 gram of fat = 9 calories (not 8—important distinction!)
Yes, fat has more than double the calories of carbs and protein, but it’s ESSENTIAL for:
- Hormone production (especially sex hormones!) 💓
- Vitamin absorption (A, D, E, K are fat-soluble)
- Brain health (your brain is ~60% fat!)
- Cell membrane structure
- Sustained energy
Types of Fat 🧈
Saturated Fat 🥥
- Found in: Butter, coconut oil, red meat, full-fat dairy, cheese
- The truth: Not the villain it was once thought to be! In moderation, it’s fine and even beneficial for hormone production
- Tip: Focus on quality sources; grass-fed butter and organic coconut oil are great choices
Unsaturated Fat (The Heart-Healthy Stars! ❤️)
Monounsaturated fats:
- Olive oil 🫒
- Avocados 🥑
- Nuts (almonds, cashews)
Polyunsaturated fats (including Omega-3s):
- Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines) 🐟
- Flaxseeds and chia seeds
- Walnuts
- Hemp seeds
Why you NEED fat: Without adequate fat, your hormones suffer, your skin gets dry, you can’t absorb vitamins properly, and you’ll feel constantly hungry! Fat also slows digestion, helping stabilize blood sugar. 🎯
⏰ Nutrient Timing: When to Eat What
🍞 Carbohydrates: Space Them Evenly!
Why? To maintain stable blood sugar throughout the day and avoid energy crashes.
Best practice:
- Distribute carbs across 3-5 meals
- Pair carbs with protein and/or fat to slow absorption
- Focus complex carbs around workouts for energy
- Avoid large carb loads at night (unless training late)
Example: Instead of eating all 200g of carbs at dinner, spread them: 40g breakfast, 50g lunch, 40g snack, 70g dinner ✅
🥑 Fats: Strategic Spacing
Why? Fat slows digestion significantly.
Best practice:
- Spread throughout the day
- Avoid excessive fat immediately pre-workout (can cause sluggishness)
- Include healthy fats with most meals for satiety
- Post-workout, keep fat moderate to allow faster carb/protein absorption
🥩 Protein: Anytime, All Day! 💯
Why? Protein has the most flexibility!
Best practice:
- Aim for 20-40g per meal for optimal muscle protein synthesis
- Can be eaten anytime without disrupting blood sugar
- Great for snacks when hungry
- Essential post-workout for recovery
- Before bed: casein protein (slow-digesting) can help overnight recovery
🎯 Putting It All Together: Your Action Plan
- Calculate your needs based on your goals (weight loss, maintenance, muscle gain)
- Track macros: Remember: 1g carbs = 4 cal, 1g protein = 4 cal, 1g fat = 9 cal
- Prioritize whole foods: Complex carbs, complete proteins, healthy fats
- Don’t fear any macronutrient—you need all three! 🌈
- Time your carbs and fats strategically around activity
- Eat protein consistently throughout the day
- Load up on fiber—it’s your digestive system’s best friend! 🙌
💡 Final Thoughts
Nutrition isn’t about being perfect—it’s about making informed choices that support your health and goals! 🎯
Remember:
- ✅ Complex carbs > simple sugars
- ✅ Fiber doesn’t count toward calorie absorption
- ✅ All three macros are ESSENTIAL
- ✅ Timing matters, especially for carbs and fats
- ✅ Quality sources make a huge difference!
Now go fuel your amazing body with knowledge AND nutrients! 🚀💪🌟
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes. Always consult with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian for personalized nutrition advice. 🏥💚